As our understanding continues to progress, the conversation surrounding medical marijuana or medical cannabis has evolved significantly. Beyond its recreational use, scientific research has shed light on the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids found in the plant, offering promising avenues for treating various health conditions. Central to this discussion is the intricate interactions between these cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system (ECS) within the human body.
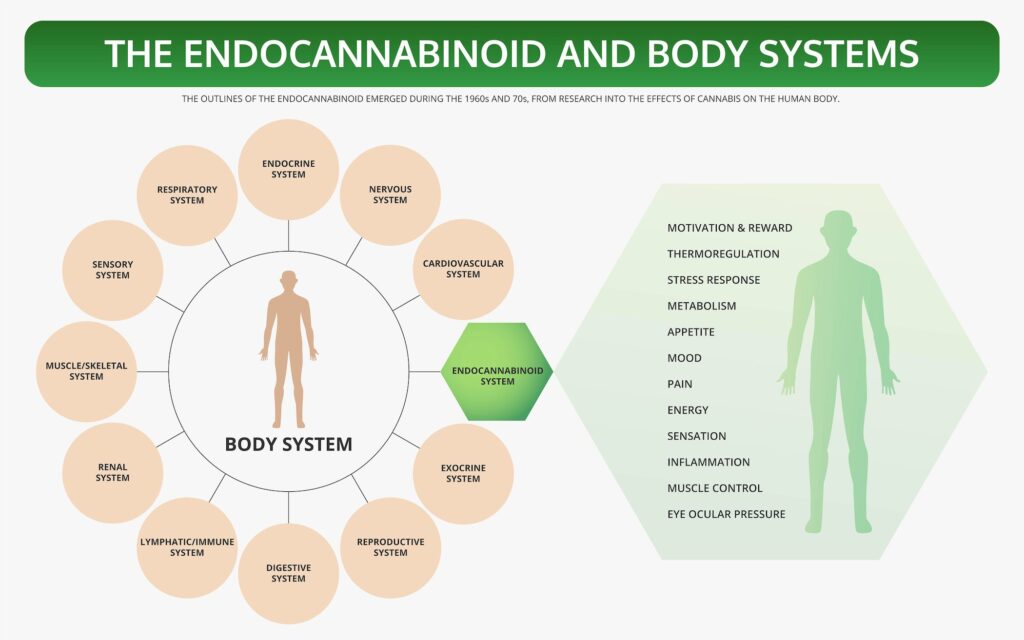
The ECS is a complex network of receptors, enzymes, and endocannabinoids that play a crucial role in regulating a range of physiological processes, including mood, appetite, pain sensation, and memory. Discovered in the 1990s, this system has since been recognized as a fundamental component of human biology, exerting influence over numerous bodily functions.
At the heart of the ECS are two primary types of receptors: CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are predominantly found in the central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are primarily located in peripheral tissues, particularly in immune cells. Endocannabinoids, which are lipid-based neurotransmitters produced by the body, bind to these receptors, initiating various cellular responses.
Medical marijuana interacts with the ECS by introducing external cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), into the body. THC, the psychoactive compound responsible for the “high” associated with medical cannabis, primarily binds to CB1 receptors, mimicking the actions of endocannabinoids. This interaction can lead to alterations in perception, mood, and cognition, making THC a target for both recreational and medicinal use.
On the other hand, CBD, a non-psychoactive compound, exhibits a more nuanced interaction with the ECS. Rather than directly binding to cannabinoid receptors, CBD modulates the activity of the ECS through various mechanisms, including enhancing the function of endocannabinoids and influencing other neurotransmitter systems. This multifaceted action has garnered significant attention for its potential therapeutic benefits across a wide range of conditions, from anxiety and depression to epilepsy and chronic pain.
When choosing the type and strength of medical cannabis to be used, the balance between THC and CBD ratios is crucial in determining the therapeutic effects and minimizing adverse side effects. For instance, strains with higher CBD content and lower THC levels are often preferred for conditions where the “high” feeling is less desirable, such as pediatric epilepsy or anxiety disorders. Conversely, conditions like chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting may benefit from higher THC concentrations to alleviate symptoms effectively.
Furthermore, the entourage effect, a phenomenon whereby the combined action of various cannabinoids, terpenes, and other plant compounds enhances the overall therapeutic efficacy of medical cannabis, underscores the importance of considering the plant’s holistic composition. By harnessing the synergistic interactions between these components, medical marijuana formulations can optimize therapeutic outcomes while minimizing potential drawbacks.
The medicinal potential of medical cannabis extends beyond symptom management to address underlying pathological processes. Preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated the anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and immunomodulatory properties of cannabinoids, suggesting their potential utility in treating conditions such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and autoimmune disorders.
Despite the growing body of evidence supporting the therapeutic benefits of medical marijuana, significant regulatory and legal barriers persist, limiting access for patients in many regions. Moreover, concerns regarding safety, standardization, and quality control underscore the need for further research and evidence-based guidelines to inform clinical practice.
In conclusion, the endocannabinoid system serves as a crucial mediator of the therapeutic effects of medical marijuana, facilitating communication between cannabinoids and various physiological processes within the body. By understanding the intricate mechanisms underlying this interaction, researchers and healthcare professionals can harness the full potential of medical cannabis-based therapies to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.